Activity 1
What was the Renaissance?
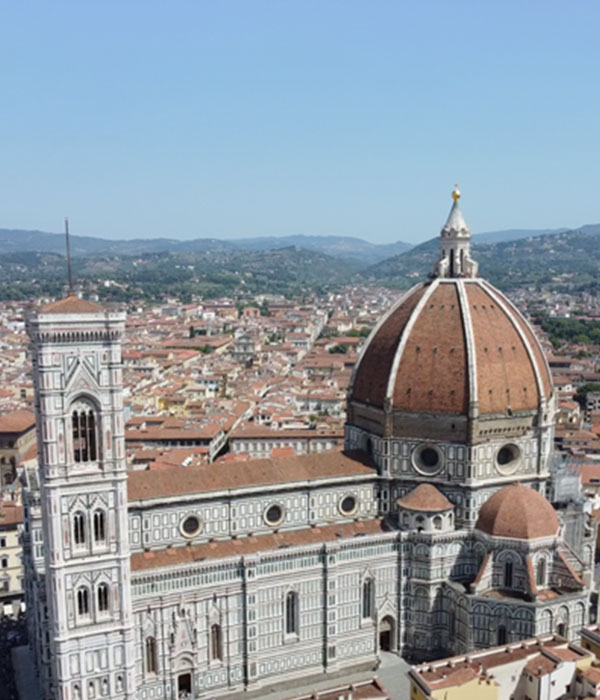
Historians describe the Renaissance as ‘possibly the most important period of development that has ever occurred in European history’. It happened between the C14th and C17th and was born in Florence, Italy and spread throughout Europe. Let’s explore this fascinating period in history. There must be lots of mysteries to uncover!
Your Task
Was the Renaissance a time of ‘milk and honey’ for all and does it still influence our lives today? Travel with Tim Gurry as he explores Florence to investigate what the city today tells us about the Renaissance of yesteryear - the legacy of famous artists and architects, the power struggles between competing families, the religious superstations, the vestiges of trade and commerce, the practice of patronage and a murder mystery that remains a cold case today.
Watch the video below. Then answer the questions below or in this Word Doc to save your answers.
What was the Renaissance really about?
What was actually ‘reborn’ during that time? Look closely at the following Renaissance images and text.
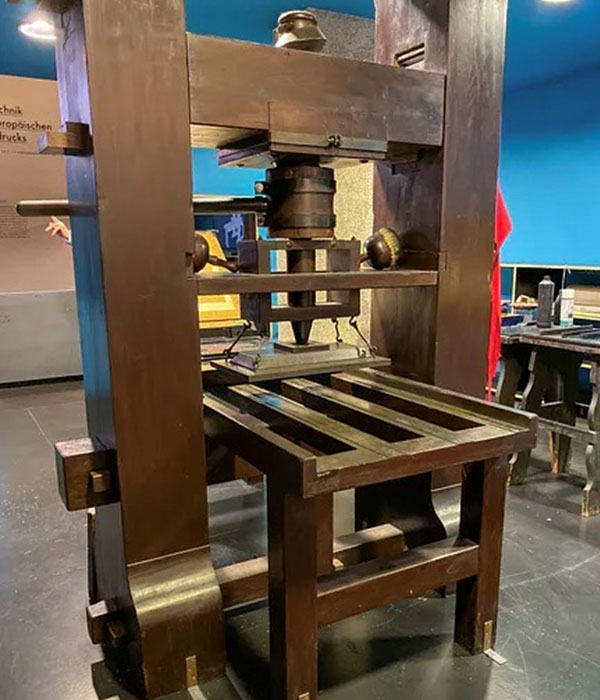
Eventually the Renaissance spread to northern Europe, ‘carried’ on trading vessels to France, Germany, England and Flanders. English Renaissance works include Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet and Thomas Moore’s book Utopia. In France Renaissance ideas influenced French writing espousing the new idea of equality of the sexes as appears in Christine de Pizan’s The Book of the City of Ladies. The invention of the printing press in Germany also helped to spread Renaissance ideas and in Flanders the painters adopted Renaissance styles and techniques still in vogue today.
Renaissance and religion
The more open thinking and new ideas of the period (humanism) challenged the teachings of the Catholic Church. People believed the church was consumed by worldly rather than Godly matters and men like Martin Luther put forward new religious philosophies demanding a return to the simplicity of the bible. Ultimately this led to what is known as the Reformation – a split in the Catholic Church and the rise of Protestantism and the Lutheran religion and other modern day denominations.
Many important events occurred throughout the Renaissance. Click on the timeline dates to discover some of the most significant and events and influential people of the Renaissance period.
1310
Giotto di Bondone revolutionised painting by making art more faithful to reality
1335
First public clock erected in Milan placed in the tower of a church and struck a bell on the hour having no dial
1347
Black Death (the plague) outbreak
1351
Giovanni Boccaccio wrote a collection of tales - a masterpiece of classical Italian prose he pioneered praise for the human ability to overcome adversity and strive for good fortune.
1421
Filippo Brunelleschi begins work on designing the dome on the Florence Cathedral
1440
Guttenberg printing press invented
1452
1452 Birth of Leonardo de Vinci
1473
The first printed book in English was published by William Caxton and Colard Mansion in Belgium
1478
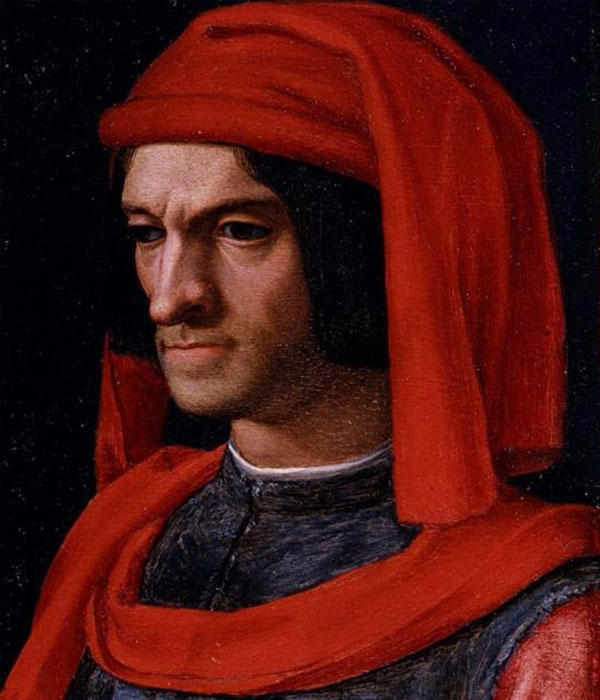
Lorenzo de Medici popularises the support of artists and inventors
1478
Spanish Inquisition begins
1492
Christopher Columbus reaches the Bahamas
1495
Leonardo de Vinci paints the Last Supper
1498
Girolamo Savonarola, the mad monk of Florence, was executed and burned for heresy.
1502
First watch is made
1503
Leonard da Vinci paints the Mona Lisa
1510
Raphael paints the School of Athens capturing the essence of the Renaissance
1512
Michelangelo finishes painting the Sistine Chapel ceiling
1517
Martin Luther wrote a theses attacking the clergy for ‘selling’ forgiveness
1534
King Henry VIII breaks away from the Catholic church
1543
Nicolaus Copernicus, astronomer, published his theory that the earth revolved around the sun
1564
Birth of William Shakespeare

DATE
Desc
Renaissance event/person |
How we live our lives today |
Lorenzo de Medici |
People of wealth today have continued the practice of supporting artists. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definitions
You often hear or read these terms/words when studying the Renaissance. Match each of the following with their correct definition.
Architecture
Sculpture
Painting
Astronomy
Invention
Industry
Literature
Banking
Church
Music
Humanism